Main Content
Social Learning and Cultural Evolution
Cultural evolution examines the social and demographic processes that explain how cultural traits change over time. Since cultural evolution allows for particularly rapid adaptation to changing environments, it provides a central explanatory approach for our evolutionary success as a species. In our work, we use theoretical models, simulations, and learning experiments to understand how social learning evolves and under what circumstances culture leads to greater adaptation and social complexity. We also use methods of cultural evolution to predict, for example, how adaptations to climate change could better spread within a population.
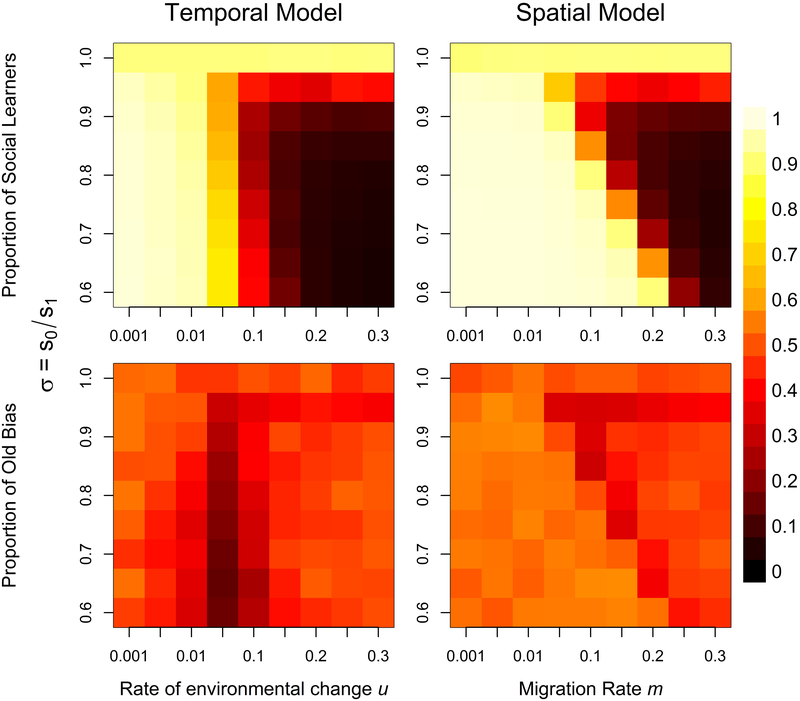
From Deffner und McElreath, 2022, PLOS One, under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
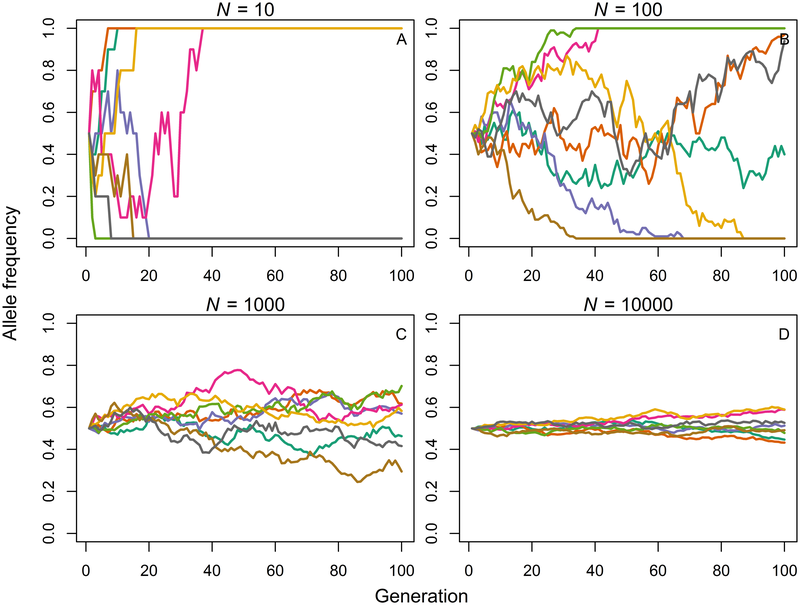
From Deffner, Kandler, & Fogarty, 2022, PLOS Computational Biology, under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Publications
- Deffner, D., Kandler, & Fogarty, L. (2022). Effective population size for culturally evolving traits. PLOS Computational Biology, 18(4).
Deffner, D., & McElreath, R. (2022). When does selection favor learning from the old? Social Learning in age-structured populations. PLOS One, 17(4). - Deffner, D., Kleinow, V. & McElreath, R. (2020). Dynamic Social Learning in Temporally and Spatially Variable Environments. Royal Society Open Science, 7(12), 200734.
- Deffner, D., & McElreath, R. (2020). The importance of life history and population regulation for the evolution of social learning. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 375(1803), 20190492.
- Deffner, D., & Kandler, A. (2019). Trait specialization, innovation and the evolution of culture in fluctuating environments. Palgrave Communications, 5-147.