B.Sc. Business Mathematics
Welcome to the web pages of the Business Mathematics Bachelor's program!
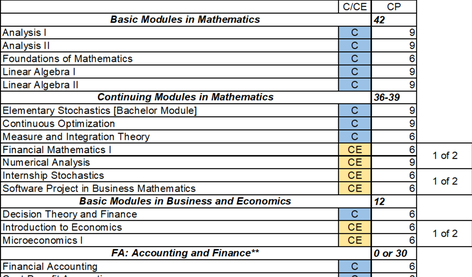
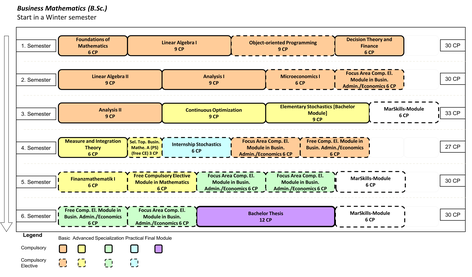
On this degree program homepage you will find all important information about studying as well as the related topics about the study requirements, the advisory services, the perspectives after the degree program as well as the application for a study place in the Bachelors's program Business Mathematics. If you have any questions or suggestions, please do not hesitate to contact our student advisory service.
Note: The main webpage of this degree programm is the German version, as it is taught in German.