16.05.2025 Paper: Influence of Pressure, Particle Morphology, Coating, and Heat Treatment on the Effective Electronic Conductivity of Cathode Active Materials for All-Solid-State Batteries
Vanessa Miß, Stefan Seus, Anna Marx, Elisa D. Steyer, Valeriu Mereacre, Joachim R. Binder and Bernhard Roling
Department of Chemistry, Philipps-Universität Marburg, Hans-Meerwein-Straße 4, 35032 Marburg, Germany
Abstract
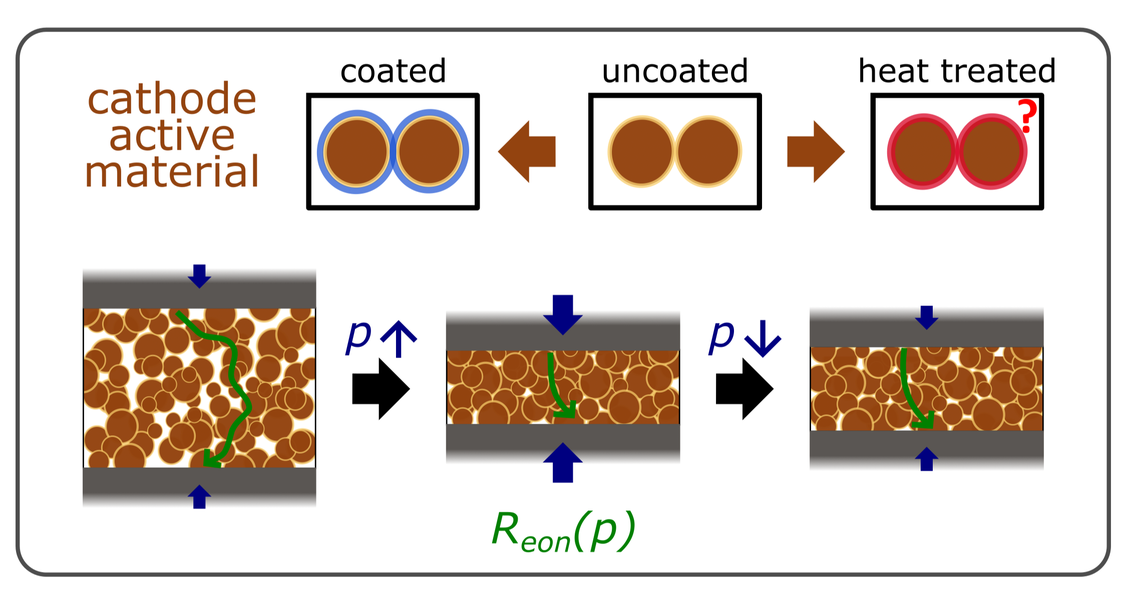
For modeling electrochemical processes in all-solid-state batteries, reliable values for the electronic conductivity of cathode active materials (CAM) are of the utmost importance. Published values for a specific CAM vary by typically many orders of magnitude. Therefore, we carried out a systematic study on the influence of various experimental parameters on the effective electronic conductivity of CAM pellets. These parameters are applied stack pressure, Ni content of CAM, CAM particle morphology, particle coating, and heat treatment. Pellets of fully lithiated and uncoated Ni-rich NMC particles reach effective electronic conductivities σeoneff in the range of 10–1 S/cm at high pressures and 10–2 S/cm at low pressures. Particle coating by LiNbO3 lowers σeoneff by half an order to 1 order of magnitude. While heat treatment at 900 °C is capable of removing surface impurities on the CAM particle, it also leads to increased Li/Ni disorder in the bulk of the particles.
Read the full paper in ACS Materials Let. 2025, 7, 2262–2269 , published by ACS Publications.
The publication was celebrated with "Puddingschnecken".